Technology Aidro: Metal 3D Printing or Additive Manufacturing AM
- Home
- Our Technology
Our Technologies
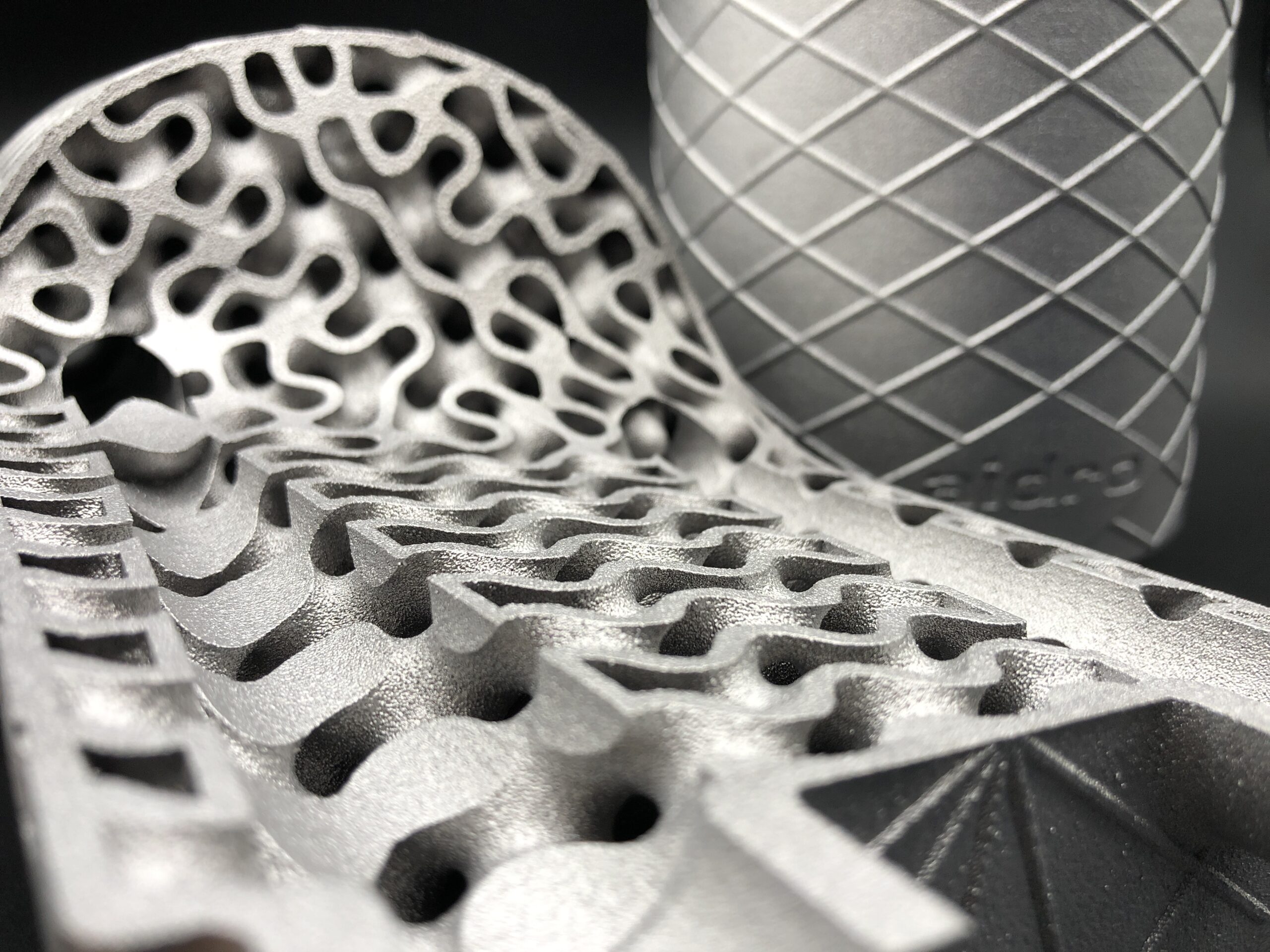
Additive manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, is a transformative approach to industrial production that enables the creation of lighter, stronger parts and systems.
Additive manufacturing uses data computer-aided-design (CAD) software or 3D object scanners to direct hardware to deposit material, layer upon layer, in precise geometric shapes. As its name implies, additive manufacturing adds material to create an object. By contrast, when you create an object by traditional means, it is often necessary to remove material through milling, machining, carving, shaping or other means.
Although the terms “3D printing” and “rapid prototyping” are casually used to discuss additive manufacturing, each process is actually a subset of additive manufacturing.
While additive manufacturing seems new to many, it has actually been around for several decades. In the right applications, additive manufacturing delivers a perfect trifecta of improved performance, complex geometries and simplified fabrication. As a result, opportunities abound for those who actively embrace additive manufacturing.
Benefits of 3D Printing
• Make possible the challenges of traditional design and manufacturing methods
• Design complex components without adding cost
• Create functional designs without manufacturing limitations
• Customize and update designs constantly
• Skip investment in manufacturing tools
• Shorter time to market
• Eliminate stock-related costs and risks
Design for Additive Manufacturing
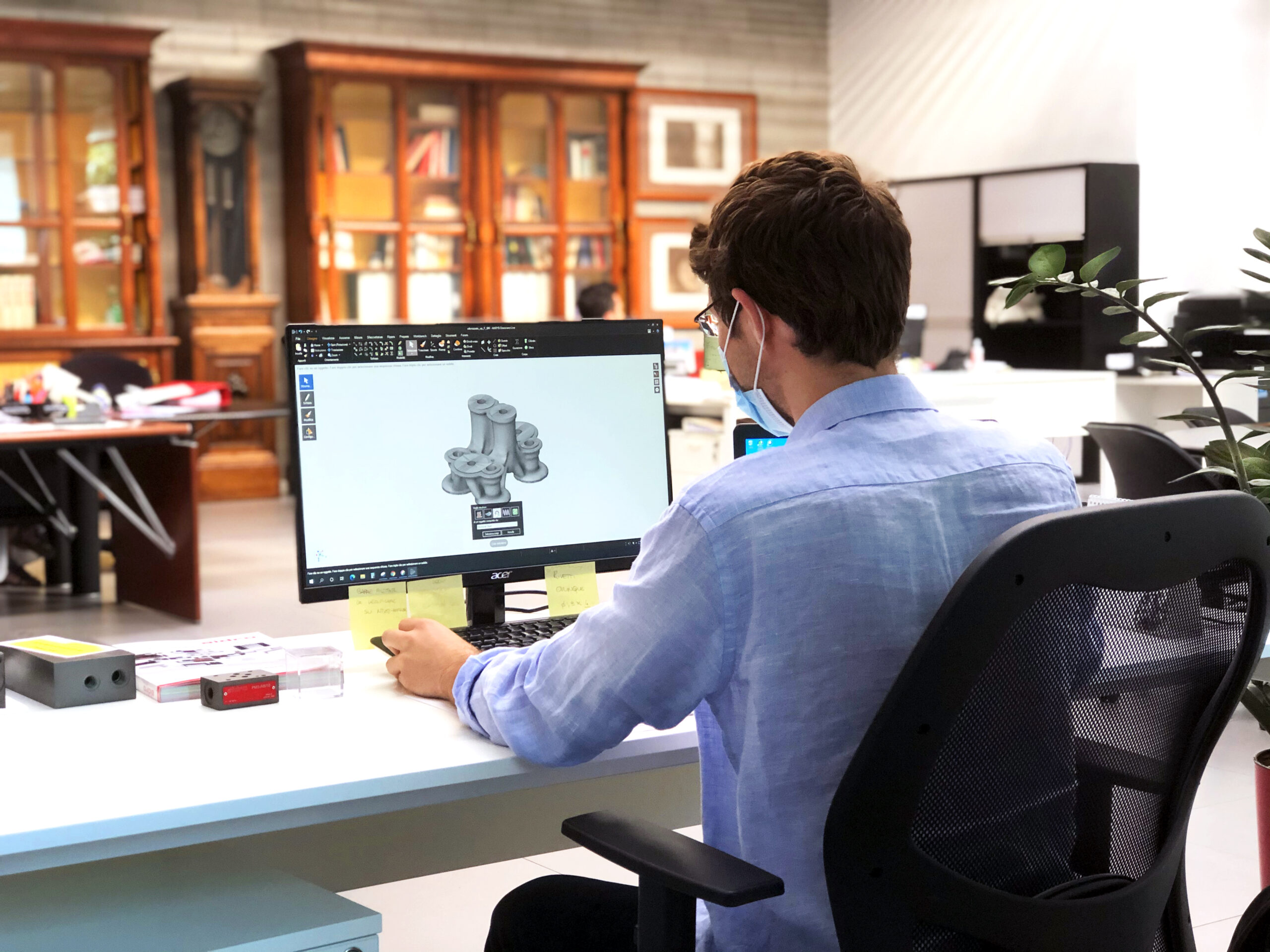



Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) is the process of adjusting your design to make it cheaper, faster, or more effective to manufacture. Executing proper design for additive manufacturing techniques can increase yield and save time and costs when building your manufacturing process by ensuring that your 3D printers are used effectively.
Technologies & Materials
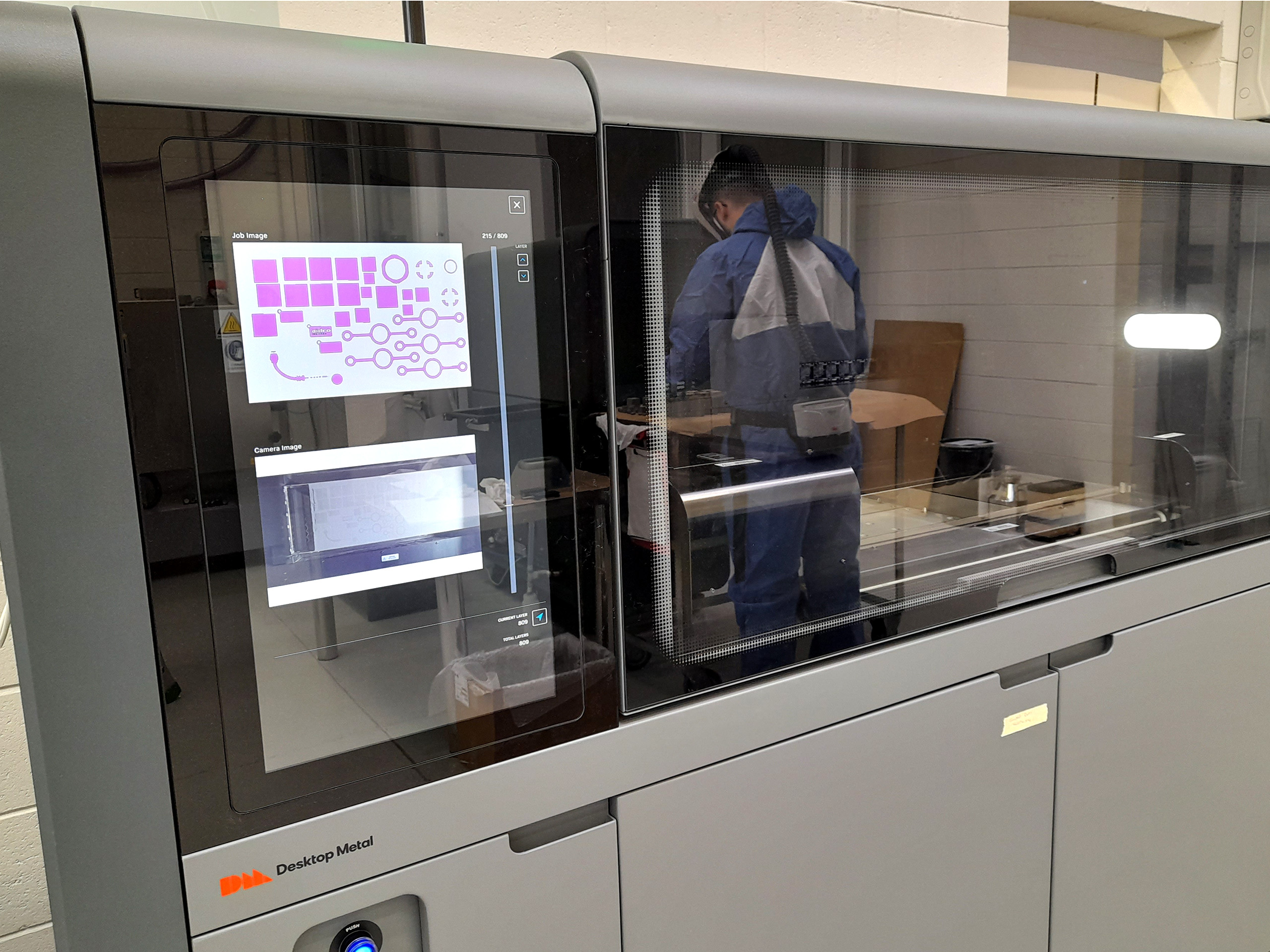





Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting is an additive manufacturing process in which an industrial printhead selectively deposits a liquid binding agent onto a thin layer of powder particles to build high-value and one-of-a-kind parts and tooling. The process is repeated layer by layer, using a map from a digital design file, until the object is complete.
Available Materials:
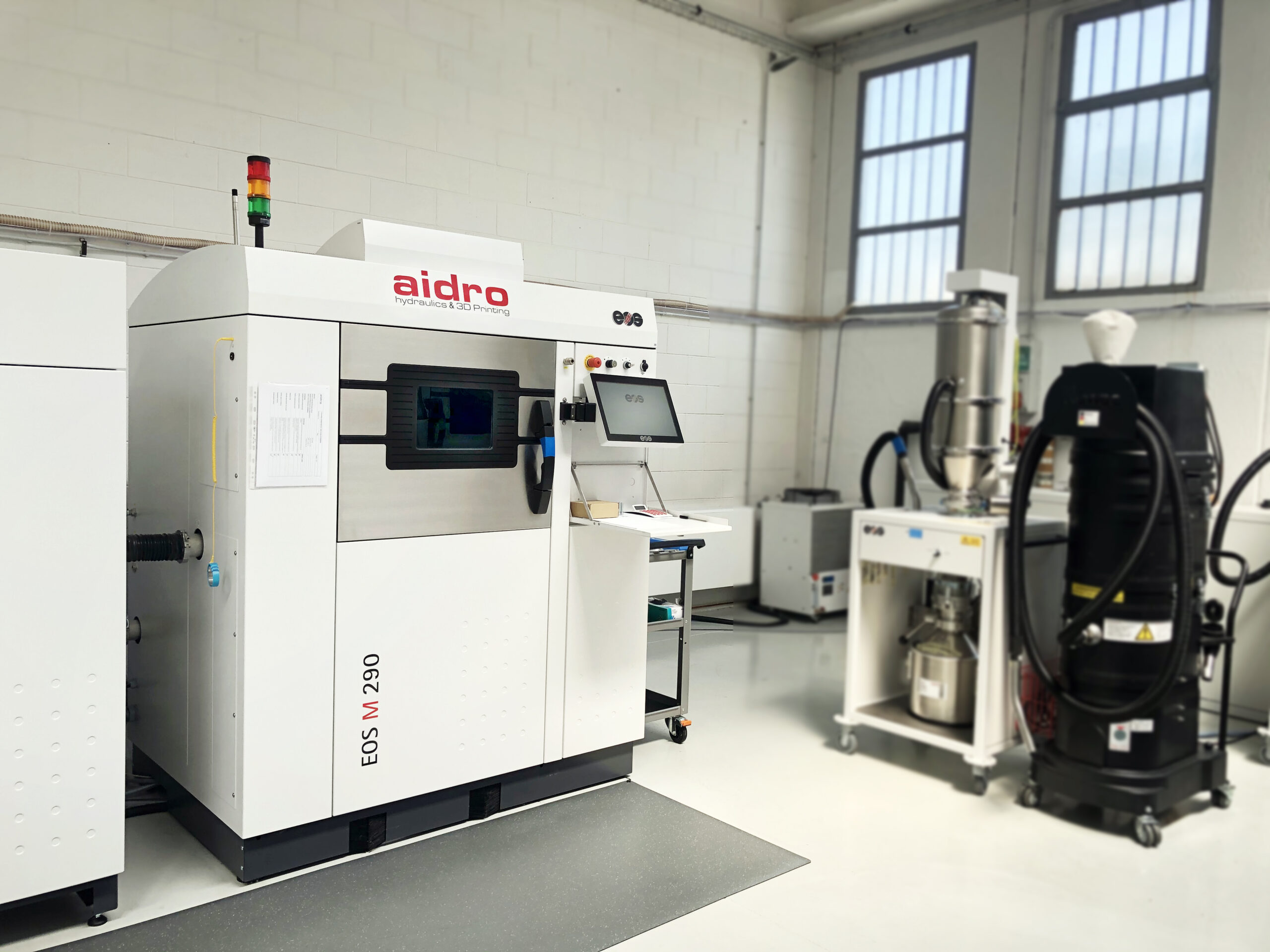
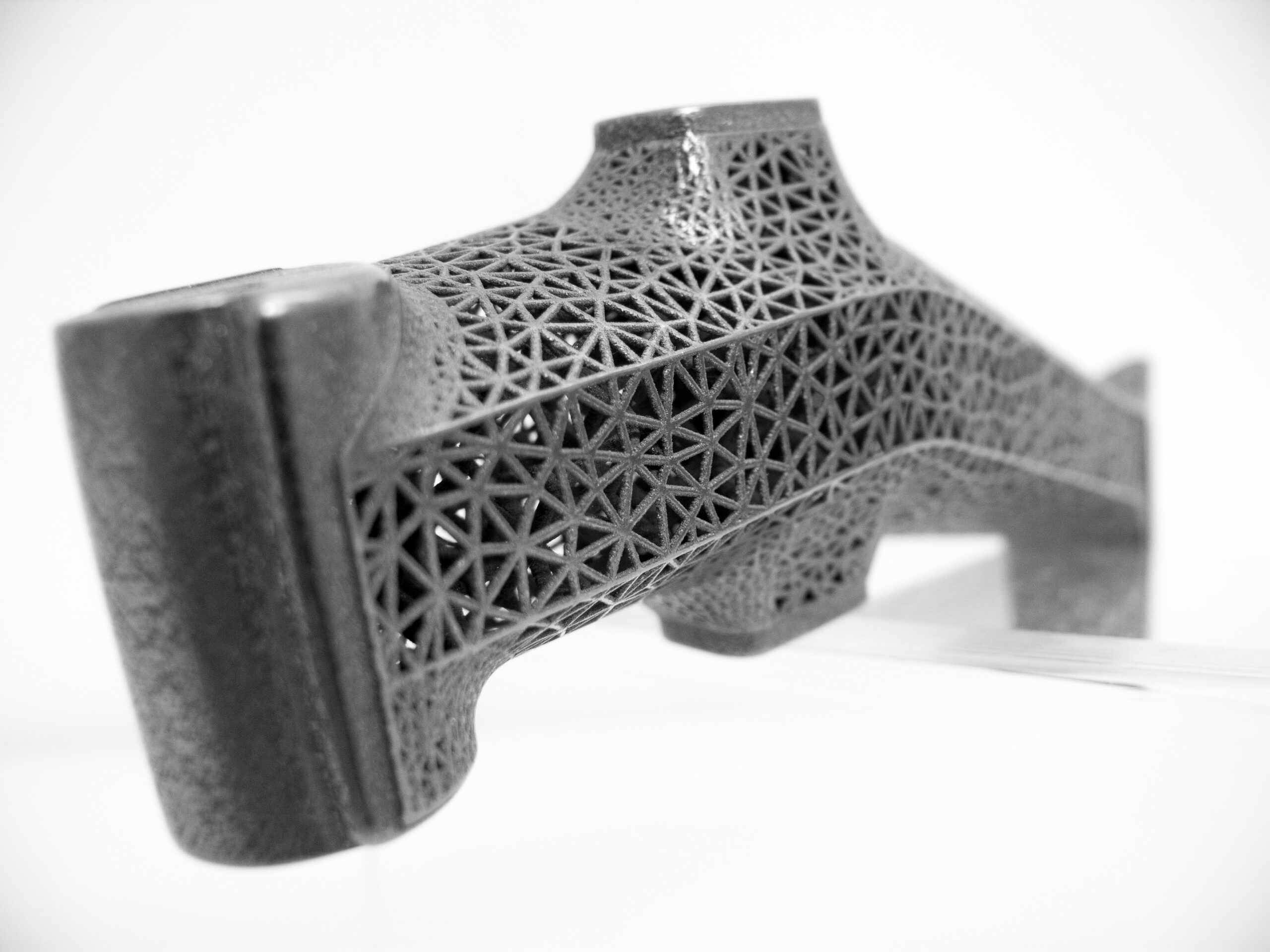
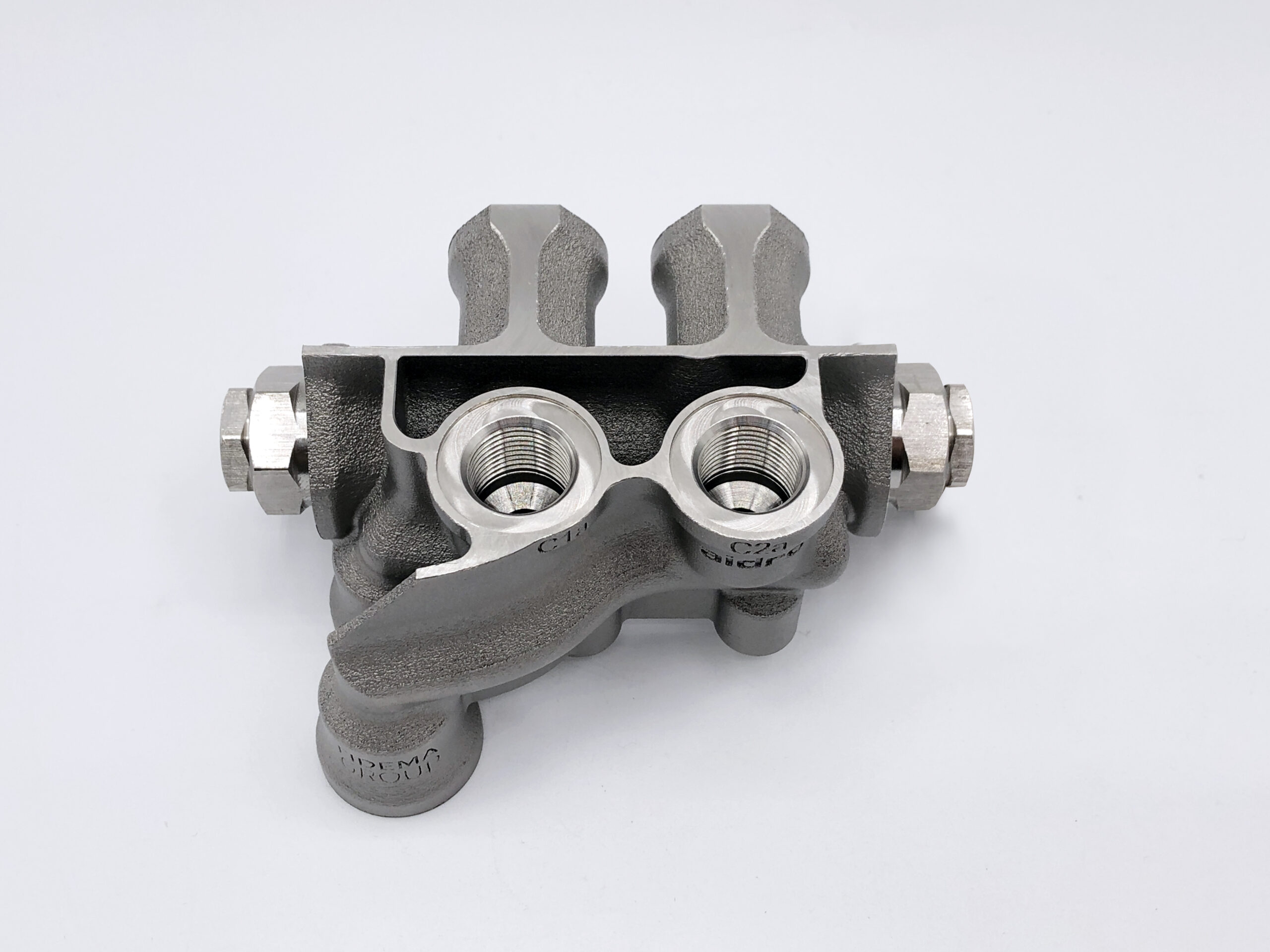
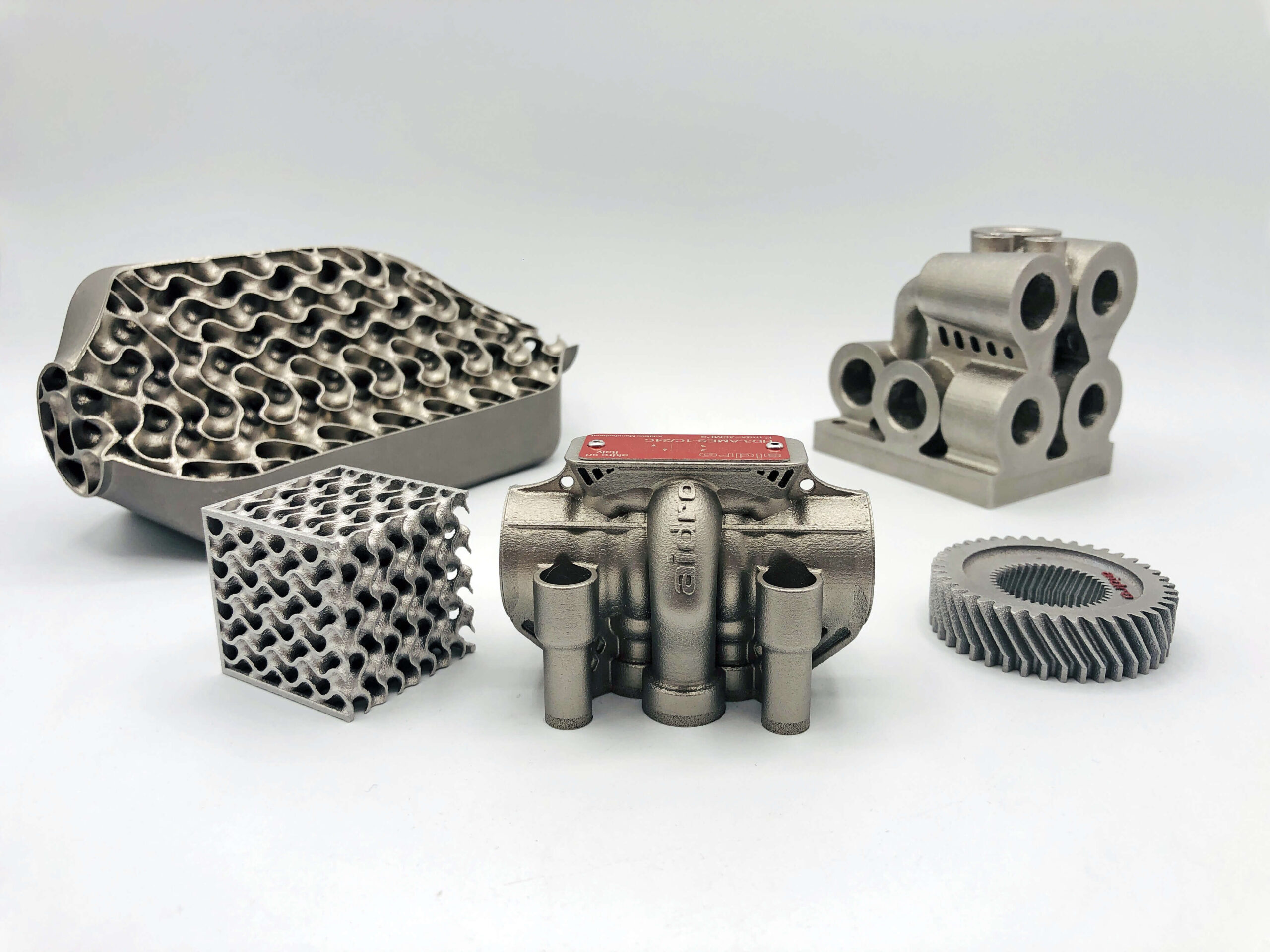





Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF)
also known as Selective Laser Melting (SLM) or Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), is among the most versatile and frequently used metal 3D printing technologies. It allows highest mechanical properties, high metal density, good surface finishing and tolerances’ respect.
Available Materials:
Other materials are available under request
AM Manufacturer Certification from DNV for two Technology
DNV has awarded two certifications – DNV-SE-0568 and DNV-ST-B203 –
for Binder Jetting Technology and Laser Powder Bed Fusion Technology.
These certifications are recognized globally and were designed in specific support of the mission-critical energy value chain, which includes the maritime and oil & gas industry.
They follow a rigorous review process by DNV, including an audit of Aidro’s facility, metal AM processes qualification, as well as qualification of parts produced by Aidro through AM methods, including mechanical, microstructural, and macrostructural tests. To achieve AMC 3 level certification for laser powder-bed fusion, DNV qualified a specific 316L part produced by Aidro for a customer, as well as a 17-4PH part for binder jetting AMC 1 level certification.
Aidro’s new DNV certifications demonstrate the company’s leadership helping energy, oil & gas, maritime, and other industries transition to Additive Manufacturing 2.0 with confidence.


REGISTERED OFFICE
Via Camperio 9
20123 Milano (MI)
Italy
HEADQUARTERS
Via Prati Bassi 36
21020 Taino (VA)
Italy
+39 0331 960250
aidro@aidro.it
LATEST NEWS
© Copyright 2021. All Rights Reserved – Aidro s.r.l. a socio unico
